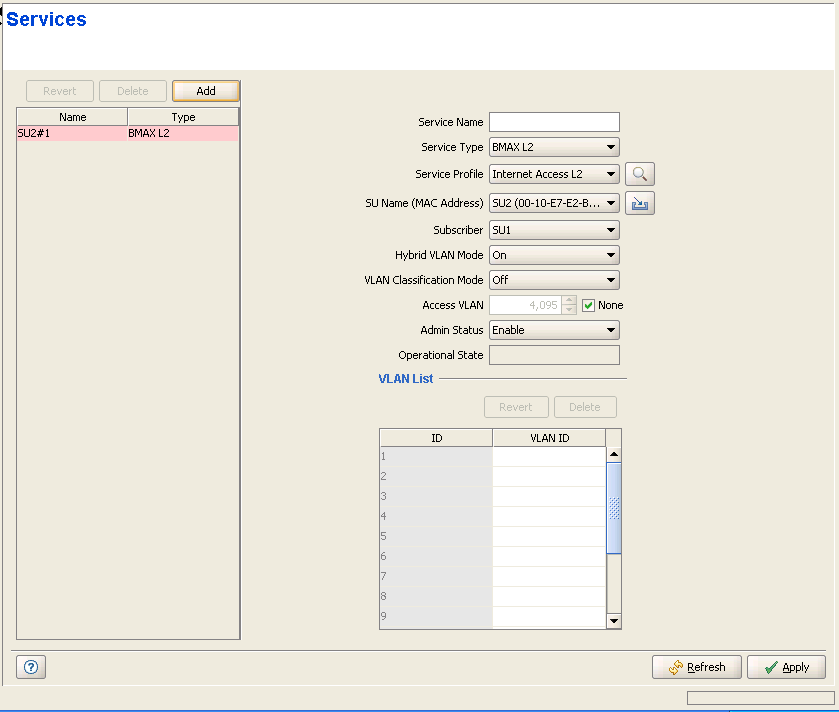
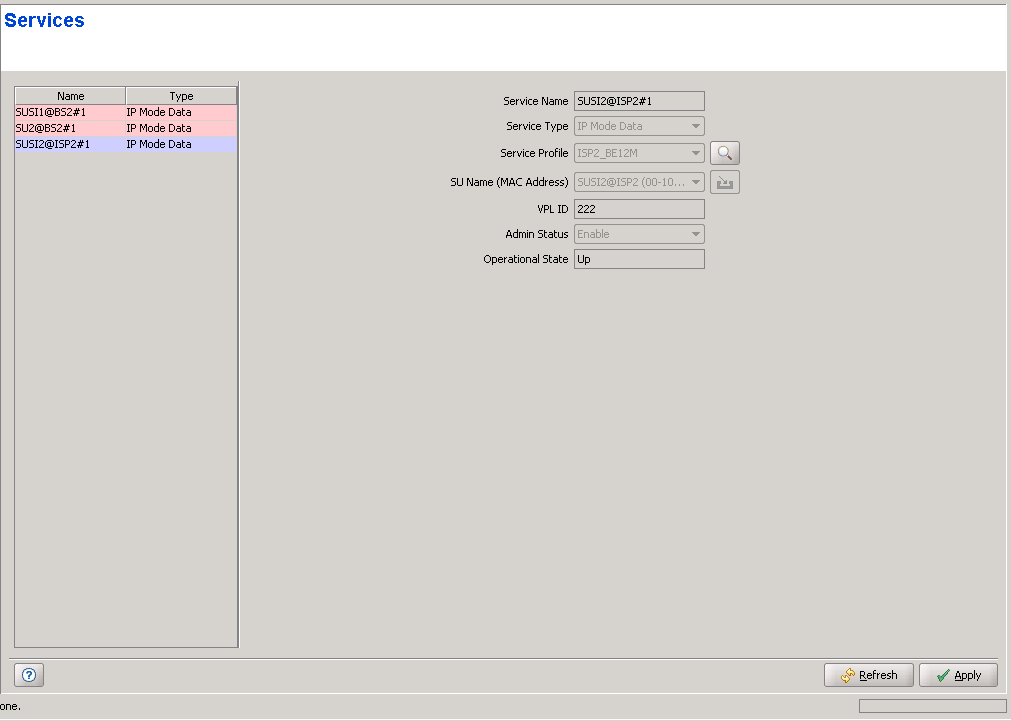
Services Page
The Services page displays a list of all Services
in the database of the device. In Ethernet CS Switching Mode it also
enables modifying existing Permanent Services, deleting Permanent Services
from the database of the device, and defining new Permanent Services.
The device can hold up to a total of 4095 Services.

|
|
A Permanent Service is a Service
defined in the device for a Permanent SU, and is applicable only in
Ethernet CS Switching Mode. A Temporary Service can be granted to a
Temporary SU by a RADIUS Authentication Server. In Ethernet CS Switching
Mode a Temporary Service may also be granted by the Base Station (based
on the Default Service Profiles) when a RADIUS server is not available,
or when the SU is rejected by the RADIUS server, provided the device
operates in Quick Service Mode and the SU uses the "quick" User Password
"quickynikinyoky". A Temporary Service is given a default name of <SU
Name>#<Number>. A Temporary Service cannot be defined, deleted
or edited.
|
The Services page comprises two sections: The Services
Table (on the left side) and the Service Editor section (on the right
side). The Editor is available only when either selecting a Service
in the Services Table or adding a new Permanent Service.
The Services table provides the following details
for each of the existing Services:
Temporary Services are displayed with a pink background.

|
To view the details of a Service:
|
Select a Service's entry. The current Service configuration
details will be displayed on the right side of the page.

|
To delete Permanent Service(s) from the
device:
|
Select one or several Service entries, click on the
Delete button and then click Apply to remove the selected
Service(s) from the database of the device. If you want to cancel the
requested delete operation before clicking Apply, click on the
Revert button.

|
To add a new Permanent Service:
|
Click on the Add button. The Service Editor
will be displayed on the right side of the page. To add a new Service
to the database of the device, fill in the necessary parameters and
click Apply.

|
To modify an existing Permanent Service:
|
Select a Service's entry. The current Service configuration
details will be displayed on the right side of the page, enabling modification
of parameters. Click Apply to update the Service's configuration.
Service Configuration Parameters:

| 
|